Multivessel Trial Results
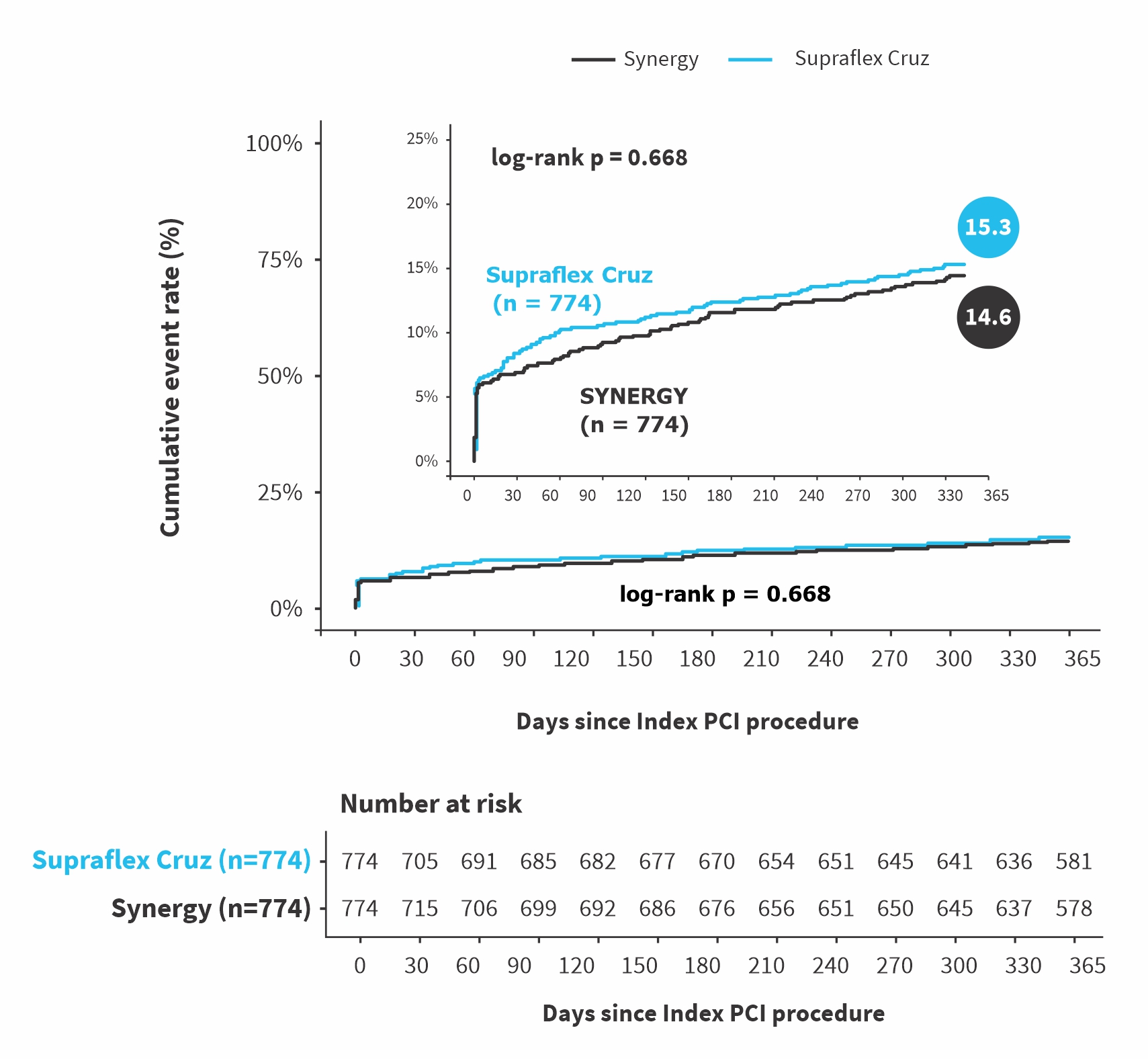
Primary endpoint of MVT trial (non-inferiority)
POCE with periprocedural MI (SCAI approach)
| Endpoint | Supraflex Cruz N = 774, n(%) | SYNERGY N = 774, n(%) | Risk Difference, % (one-sided 95%CI) | P-value non-inferiority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POCE with non-inferiority margin of 40% of the assumed event rate (10.7%) | 117(15.3%) | 111(14.6%) | 0.73 % (NA to 3.73) | 0.026 |
| POCE with non-inferiority margin of 40% of the observed event rate (14.6%) | 117(15.3%) | 111(14.6%) | 0.73 % (NA to 3.73) | <0.001 |
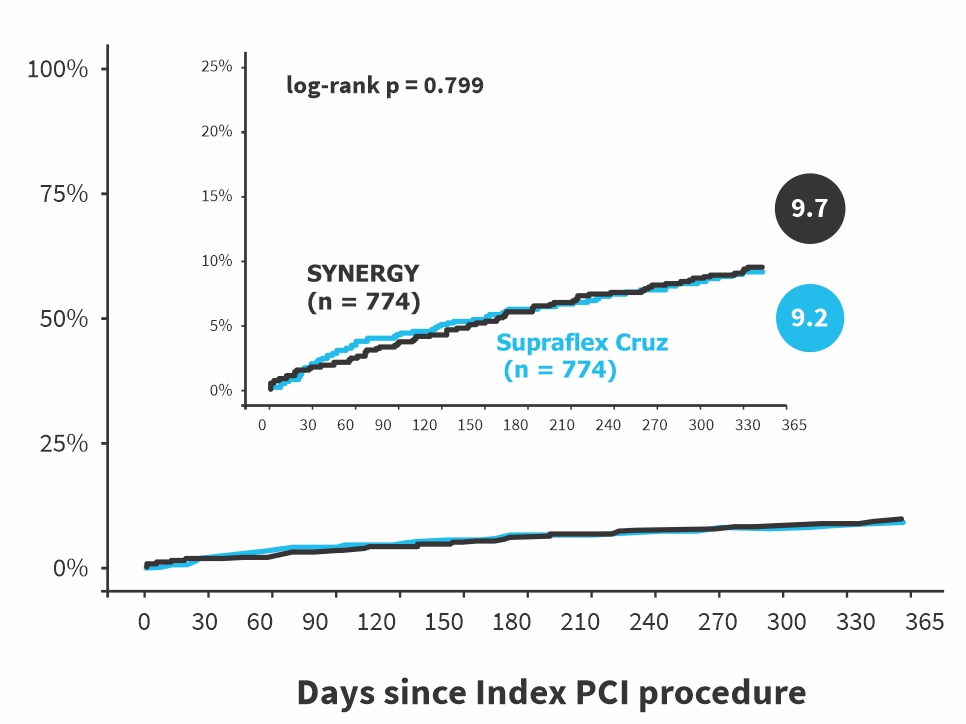
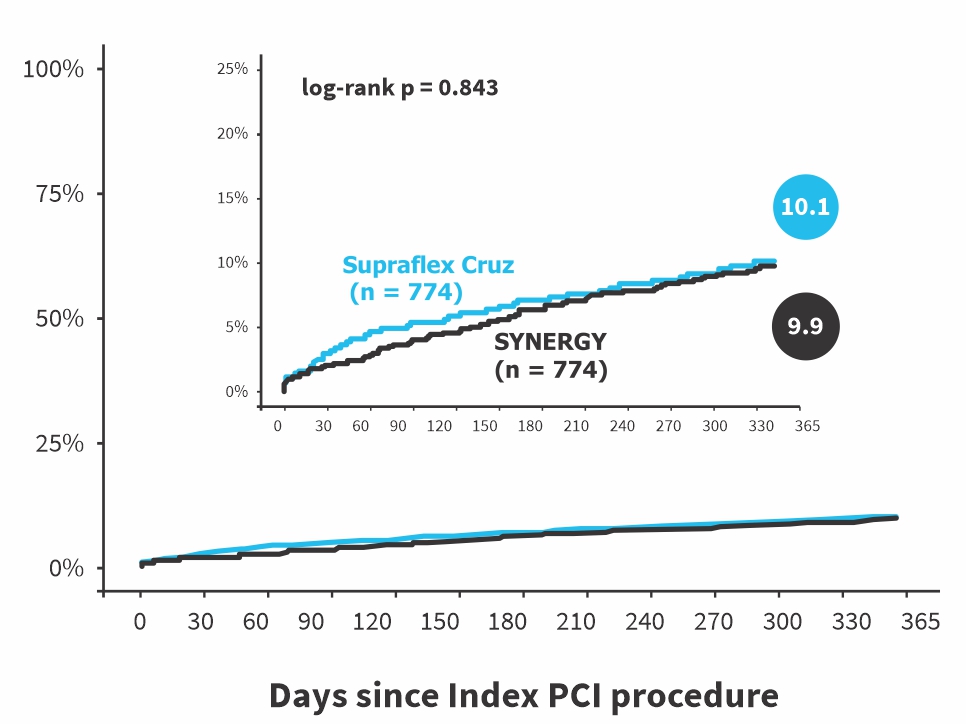
POCE with different definition of periprocedural MI (sensitivity-analysis)
| POCE at 1 year with different definition of periprocedural MI | Supraflex Cruz N = 774, n(%) | SYNERGY N = 774, n(%) | Risk Difference, % (95%CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| periprocedural MI = NOBLE1 | 70 (9.2%) | 73 (9.7%) | -0.46 (-3.40 to 2.49) | 0.763 |
| periprocedural MI = SYNTAX2 | 77 (10.1%) | 75 (9.9%) | 0.19 (-2.83 to 3.22) | 0.899 |
| periprocedural MI = 4th universal definition3 | 166 (21.7%) | 169 (22.1%) | -0.45 (-4.60 to 3.69) | 0.831 |
- N Engl J Med. 2016 Dec 8;375(23):2223-2235. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1610227.
- N Engl J Med. 2009 Mar 5;360(10):961-72. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0804626.
- Circulation. 2018 Nov 13;138(20):e618-e651. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000617.
| Endpoint | Supraflex Cruz N = 774, n (%) | SYNERGY N = 774, n (%) | Risk Difference, % (two-sided 95% CIs) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POCE (all-cause death, any stroke, any MI, any revascularization) | 117 (15.3%) | 111 (14.6%) | 0.73 % (-2.86 to 4.31) | 0.691 |
| All-cause death | 24 (3.2%) | 22 (2.9%) | 0.24 % (-1.49 to 1.96) | 0.787 |
| Any stroke | 1 (0.1%) | 3 (0.4%) | -0.27 % (-0.79 to 0.25) | 0.316 |
| All-cause death and Stroke | 24 (3.2%) | 24 (3.2%) | -0.03 % (-1.79 to 1.73) | 0.977 |
| Any Myocardial infarction (MI) | 77 (10.1%) | 62 (8.2%) | 1.94 % (-0.96 to 4.84) | 0.190 |
| All-cause death, any Stroke and any MI | 92 (12.0%) | 82 (10.8%) | 1.26 % (-1.93 to 4.45) | 0.439 |
| Any revascularization | 48 (6.5%) | 51 (6.9%) | -0.42 % (-2.96 to 2.12) | 0.745 |
| BARC 2,3, or 5 bleeding | 49 (6.5%) | 49 (6.5%) | 0.04 % (-2.44 to 2.52) | 0.977 |
| BARC 3 or 5 bleeding | 22 (2.9%) | 34 (4.5%) | -1.57 % (-3.47 to 0.32) | 0.104 |
| NACE (all-cause death, any stroke, any MI, any revascularization and BARC bleeding 3/5) | 119 (15.6%) | 113 (14.8%) | 0.72 % (-2.88 to 4.32) | 0.695 |
Conclusion
The screening was based on visual assessment of stenotic lesions (DS ≥50%) by the investigators, but many of the so-called 3VD, when investigated by physiology (QFR), were in fact 1- or 2VD, and only 35% were true 3VD from a functional point of view as in the SYNTAX-II trial* (37%, with combined iFR and FFR)
In 3VD patients treated with “State of the Art” PCI, the Supraflex Cruz is non-inferior to the SYNERGY in terms of PoCE at 1-year.
PPMI with its various definitions (Noble, SCAI, SYNTAX I, ARC-II, 4th UDMI) is a confounding factor. When removed from the composite endpoint (Noble approach), the rate of PoCE in the Supraflex Cruz (9.2%) and SYNERGY (9.7%) underscores the safety of performing 3VD PCI in patients with SYNTAX Score ranging from less than 22 to more than 32.
* Eur Heart J. 2017 Nov 7;38(42):3124-3134. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx512.
Additional Information
Baseline Characteristics
| Characteristics | Supraflex Cruz N = 774 | SYNERGY N = 774 |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 68.2 | 67.9 |
| Male | 74.9 % | 77.5 % |
| Body-mass index (kg/m2) | 28.3 | 28.4 |
| Hypertension | 79.2 % | 79.7 % |
| Hyperlipidemia or Hyperlipidemia treatment | 74.5 % | 80.4 % |
| Diabetes | 36.0 % | 35.1 % |
| - Insulin Dependent | 10.7 % | 9.7 % |
| Family History of Coronary Artery Disease | 27.0 % | 30.2 % |
| Current Smoker | 20.5 % | 19.6 % |
| High bleeding risk (ARC-HBR) | 18.5 % | 18.7 % |
| Creatinine Clearance ≤ 60 ml/min | 18.7 % | 18.7 % |
| Heart Failure | 19.3 % | 17.3 % |
| Peripheral Vascular Disease | 10.5 % | 10.2 % |
| Atrial Fibrillation | 9.0 % | 9.8 % |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | 7.0 % | 7.5 % |
| Previous Myocardial Infarction | 4.3 % | 4.1 % |
| Chronic Coronary Syndrome (CCS) | 48.8 % | 47.8 % |
| NSTE-ACS (based on biomarkers) | 51.2 % | 52.2 % |
| - NSTEMI | 38.1 % | 41.2 % |
| - Unstable angina | 13.0 % | 11.0 % |
| Reduced LVEF (<50%) | 19.3 % | 19.1 % |
| Use of long-term oral anticoagulation | 7.9 % | 8.3 % |
| Presence of CTO (per patient) | 26.0 % | 25.2 % |
| Presence of Bifurcation Lesion (per patient) | 73.0 % | 74.2 % |
| Anatomical SYNTAX Score (core lab report) | 20.0 (14.0-26.0) | 20.0 (15.0-27.0) |
| Functional SYNTAX Score (core lab report) | 19.0 (13.0-25.5) | 18.5 (13.0-26.0) |
| Predicted 1-year mortality* (Logistic clinical SYNTAX) | 3.3 % (3.1-3.6) | 3.3 % (3.1-3.6) |
* Eur Heart J. 2012 Dec;33(24):3098-104. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs295.
Abbreviation: CK-MB: Creatine Kinase–Myocardial Band, ULN: Upper Limit of Normal, NACE: Net Adverse Clinical Events, iFR: Instantaneous Wave-Free Ratio, FFR: Fractional Flow Reserve, QFR: Quantitative Flow Ratio, UDMI: Universal, Definition of Myocardial Infarction, PPMI: Periprocedural Myocardial Infarction, NSTE-ACS: Non–ST-Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome, NSTEMI: Non–ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction, CTO: Chronic Total Occlusion